|
Advanced Geological Services |
|
Providing Comprehensive Geophysical Solutions |

|
Advantages: |
|
EM equipment utilized by AGS is lightweight and easily transportable. Data for a large area can be collected rather quickly. The topography can be uneven and can be covered with higher vegetation. |
|
Limitations: |
|
Interference from surface or near surface metallic objects. Sources of interference can include: buildings, metal fences, vehicles, buried pipes and cables, large metal objects and overhead electrical wires. While these objects may interfere with certain types of investigations, EM can be used successfully to map their locations as well. |
|
AGS Personnel Using an EM-61 |

Applications and Methods: |
|
Electromagnetic (EM) methods employed by AGS are useful for the following: · Delineate and map landfill boundaries and cells · Locate and map contamination plumes · Locate and delineate buried metal objects, USTs, and storage drums · Locate and map metallic utilities and pipes · Delineate and map previously excavated and backfilled areas EM is a geophysical technique based on the physical principles of inducing and detecting electrical current flow within geologic strata. EM induction surveys work by inducing time-varying magnetic fields into the ground from a transmitter coil. The resulting secondary electromagnetic field set up by ground conductors is then measured at a receiver coil. The presence of metals, ions, or clays increase the ground conductivity. Depth range of EM instruments is a function of the degree of separation between the transmitter and receiver coils. |
|
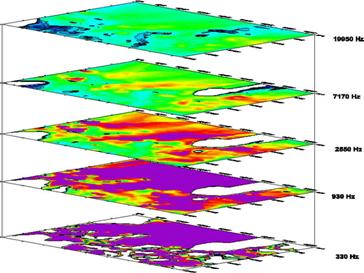
Sample EM Color Contour Map at Different Frequencies Corresponding to Various Depths Below Ground Surface |
|
Electromagnetic (EM) |

|
Foundation Debris Detected with the Electromagnetic Method (Click to Enlarge) |