|
Limitations: |
|
Resistivity surveys require a fairly large area far removed from power lines and grounded metallic structures. Profiling surveys can be more labor intensive than some other geophysical survey methods. |
|
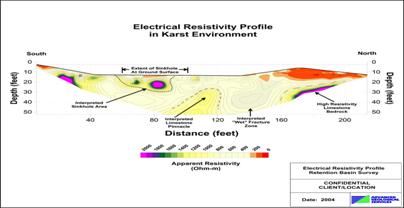
Sample Electrical Resistivity Profile Results (Click image to enlarge…) |
|
Advanced Geological Services |
|
Providing Comprehensive Geophysical Solutions |

|
Advantages: |
Applications and Method: |
|
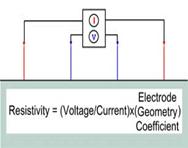
The Electrical Resistivity method is useful for the following: · Characterize subsurface hydrogeology · Locate water bearing zones · Determine depth to groundwater · Evaluate electrical grounding characteristics · Map stratigraphy · Map clay aquitards · Map salt-water intrusion · Map vertical extent of certain types of soil and groundwater contamination · Estimate landfill thickness · Determine depth to bedrock/overburden thickness · Map faults · Map lateral extent of conductive contaminant plumes · Delineate disposal areas Electrical or direct current methods measure the bulk resistivity of the subsurface to determine geologic structure and/or physical properties of the geological materials. An electrical current is introduced directly into the ground through current electrodes. The resulting voltage potential difference is measured between a pair of potential electrodes. The current and the potential electrodes are generally arranged in a linear pattern. The apparent resistivity is the bulk average resistivity of all soils and rock influencing the flow of current. |
|
Substantial quantitative computer modeling is possible. The resulting models can provide accurate estimates of depths, thickness and electrical resistivities of subsurface layers. Surveys can be completed to depths of several hundred feet. Large distances can be covered in a relatively short period of time. |
|
Electrical Resistivity |